The UAE is pairing traditional and alternative energy sources to sustainably produce the power needed to fuel its economy. The UAE’s Net Zero by 2050 Strategic Initiative – is working to expand innovation across the energy sector.
The UAE has taken aggressive action to diversify the UAE energy mix and economy. Today, oil and gas exports account for about 30 percent of the UAE’s total economic activity. The share of additional energy sources is rapidly expanding to meet growing energy demands.
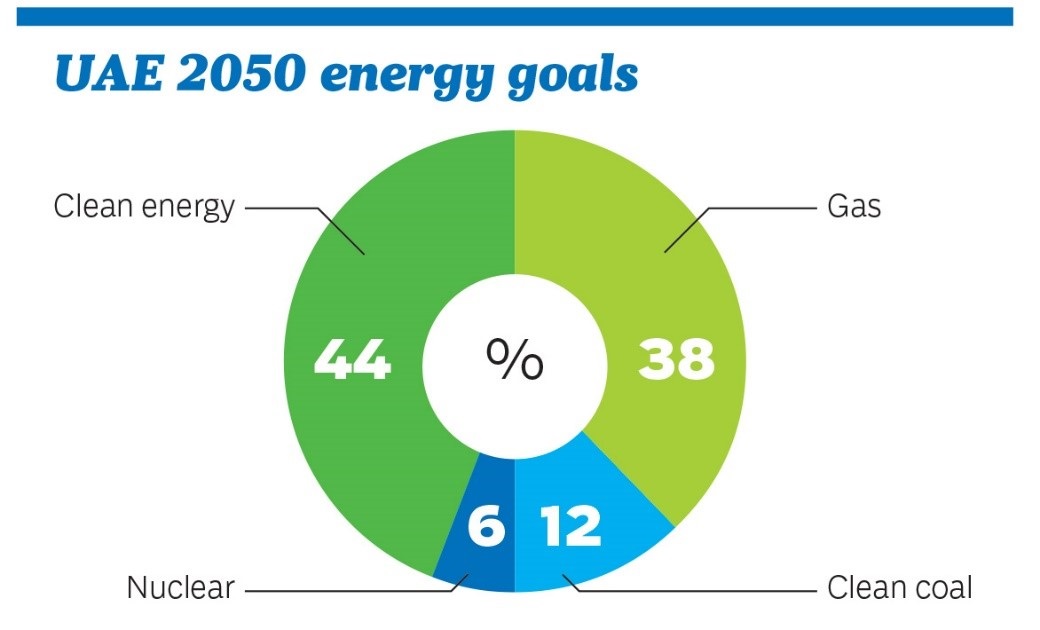
UAE 2050 Energy Goals
The UAE Energy Strategy 2050 targets an energy mix that combines commercially-viable renewable, nuclear and alternative energy sources to meet the UAE’s economic requirements and environmental goals as follows:
- 44 percent alternative energy
- 38 percent gas
- 12 percent clean coal
- 6 percent nuclear
In 2023, the UAE updated its National Energy Strategy to include several new goals, including:
- Create 50,000 new jobs by 2030
- Triple renewable energy capacity to 14 GW by 2030
- Raise the percentage of alternative energy in the total energy mix to 30% by 2031
- Become carbon-neutral by 2050
Diversifying the UAE Energy Mix
At home, the UAE is building a more resilient energy sector through the development of additional energy sources.
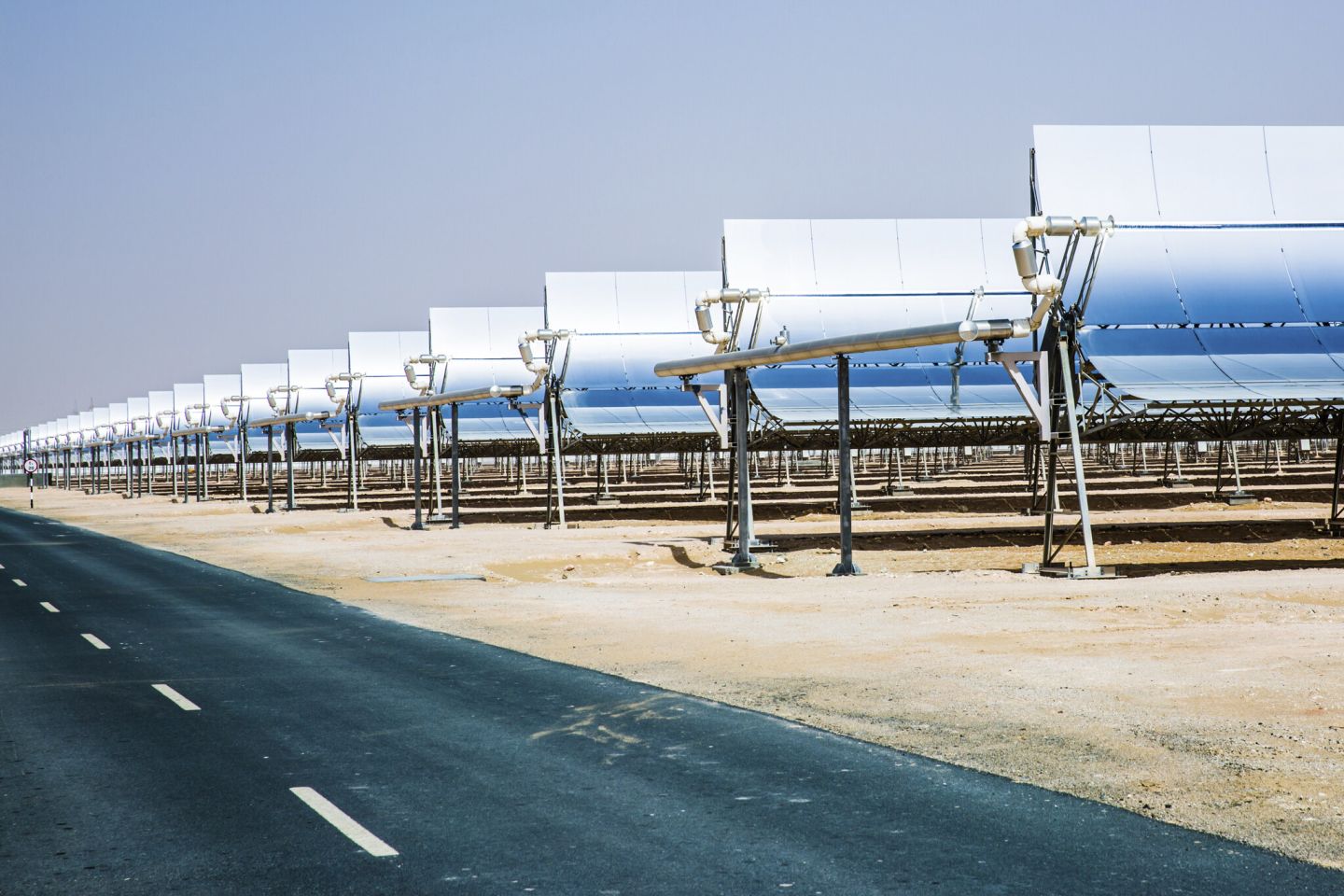
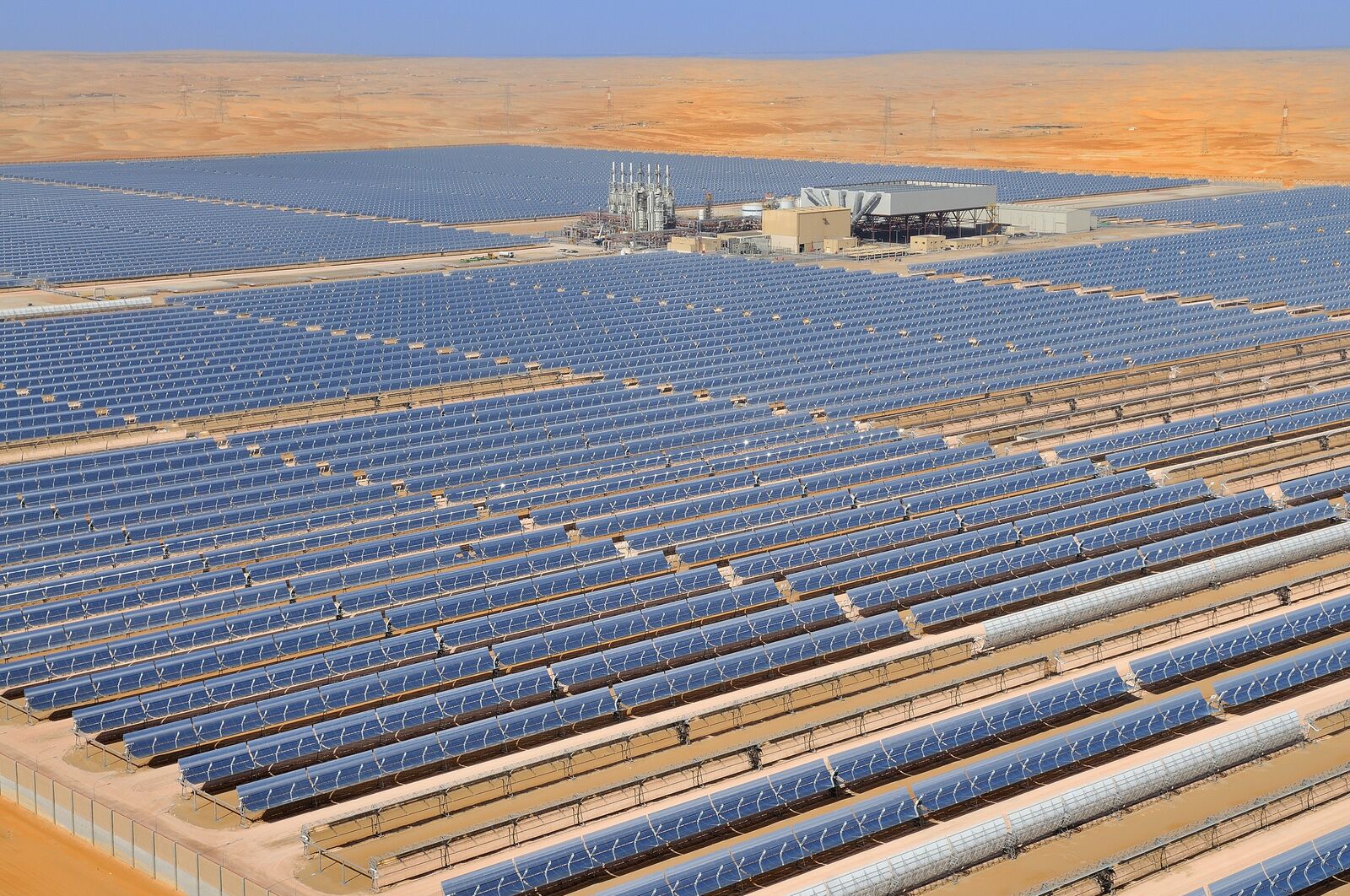
- Solar Energy: The UAE has three of the world’s largest solar plants, including the world’s largest single-site solar plant – Al Dhafra Solar PV. The other plants include the Noor Abu Dhabi solar park, which will reduce the UAE’s carbon footprint by 1 million metric tons per year, and the Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park in Dubai, which will generate enough solar energy to power 800,000 homes by 2030.
- Nuclear Energy: The UAE is the first Arab country to operate a nuclear energy plant. The UAE’s nuclear energy program provides 25% of the country’s total electricity needs.
- Carbon Capture: The UAE is pragmatic about the present because even in the swiftest energy transition scenario the world will still need oil. The UAE is the first country in the region to deploy industrial-scale carbon capture technology. ADNOC is currently developing the largest carbon capture project in the Middle East and North Africa. Once completed, the project will store 1.5 million tons of carbon annually.
- Wind Energy: In October 2023, the UAE launched its first wind power program. The 104-megawatt (MW) landmark project has been developed across four locations in the UAE and is expected to power over 23,0000 UAE homes and displace 120,000 tons of CO2 per year.
- Hydrogen: The UAE is scaling up its blue and green hydrogen production. The country’s National Hydrogen Strategy 2050 that aims to enhance the UAE’s position as one of the largest producers of hydrogen by 2031.
Continue reading for more detailed information on each of these sectors.

Alternative Energy Investment
Under its National Energy Strategy, the UAE invest $54 billion to meet growing energy demands.
Through over 15 years of R&D and policy work, solar is available at 1.35 cents per kilowatt hour. The UAE has three of the world’s largest solar plants.
- The Noor Abu Dhabi solar park has a total capacity of 1.2 GW.
- In Dubai, the 4,000-acre Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park, the largest solar park in the Middle East, will generate enough solar energy to power 800,000 homes by 2030.
- The UAE’s Wind Program, developed by Masdar, will introduce wind power to the UAE’s electricity grid, diversifying the country’s energy mix.
- Abu Dhabi committed more than $20 billion to renewable energy programs through Masdar, which focuses on the development and commercialization of technologies in energy efficiency, carbon management and monetization, water usage and desalination.

Nuclear Energy
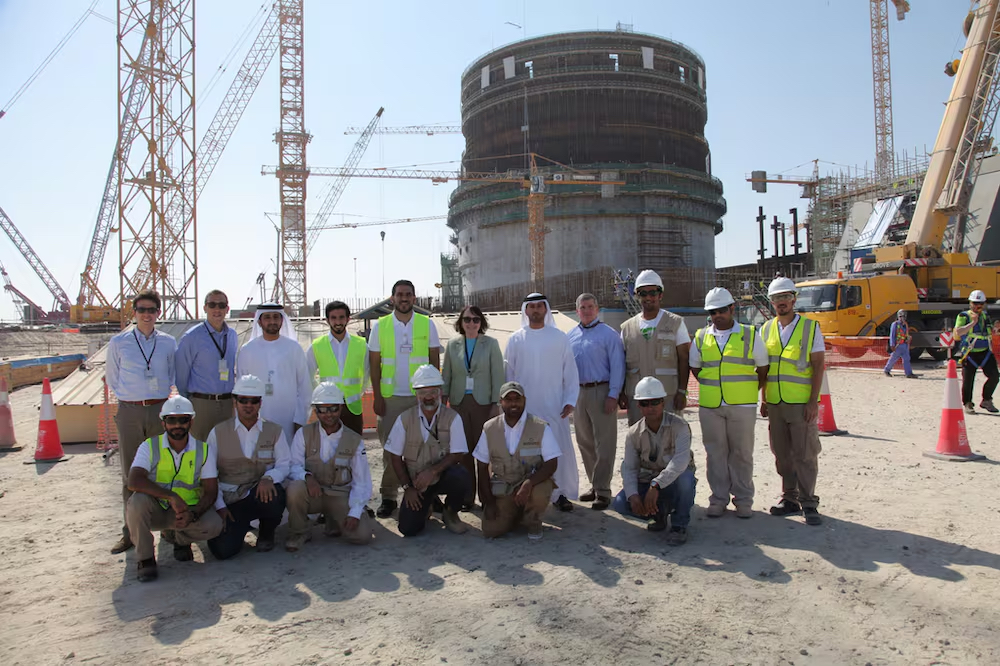

Nuclear energy is contributing to a diversified, secure energy mix in the UAE. With rigorous regulatory standards and strong management, the UAE’s nuclear program stands out as a global leader in safety and sustainability.
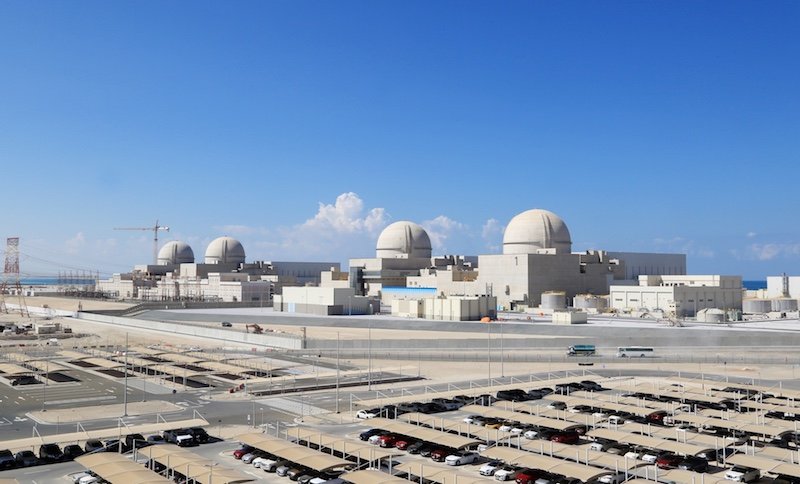
Working with a consortium led by Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) that includes US partners, the UAE built and brought online four reactors at the Barakah Nuclear Power Plant in Abu Dhabi. The Barakah Plant is the first nuclear energy plant in the Arab World. With four commercially operational reactors, the plant generates 40TWh of energy annually, the equivalent of powering 500,000+ homes.
Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation (ENEC), the operator of the Barakah Plant, is a global leader in nuclear energy innovation, deploying smart technology across the sector through its ADVANCE Program. Partnerships with US companies such as Terra-Power, X-Energy and Westinghouse are exploring advanced nuclear reactor technologies with the potential to decarbonize heavy industries.
123 Agreement
In December 2009, the UAE and US signed a “123 Agreement” that established a legal framework for peaceful nuclear cooperation between the two countries. In the agreement, the UAE voluntarily committed to the highest possible standards of nuclear nonproliferation, safety and security. Regarded as the “gold standard” for civilian nuclear energy development and cooperation with the US, the landmark US-UAE 123 Agreement has been hailed as best practice by US officials across administrations, as well as by nonproliferation experts for its commitment to safety, security and operational transparency. The peaceful nature of the UAE’s nuclear energy ambitions are also enshrined in UAE law, including the 2009 UAE Nuclear Law.
As outlined in the US-UAE 123 Agreement, the UAE’s nuclear energy program is overseen by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and upholds strong nonproliferation guarantees – including forgoing domestic uranium enrichment and reprocessing. The IAEA and the World Association of Nuclear Operators (WANO) have conducted regular reviews of the UAE Program, the Barakah Plant and its operations team to ensure all activities are aligned with international best practices.
The US-UAE 123 Agreement paved the way for bilateral nuclear cooperation, which has generated over $2.75 billion in contracts for the US private sector. Spanning 175 companies across 33 states, collaboration with US firms has ranged from manufacturing and engineering support to operational oversight and development of safety standards. US firms involved in the UAE nuclear energy program include:
- Westinghouse, headquartered in Cranberry, Pennsylvania, is part of a consortium led by Korea Electric Power Corporation and has provided major components; instrumentation and control equipment; and design technical and engineering support services.
- Virginia-based Lightbridge Corporation has provided consulting services to the UAE on the design, development and management of the key organizations required to implement a nuclear energy program according to the highest international standards.
- Englewood, Colorado-based CH2M Hill won a 10-year contract to support the UAE's nuclear program in October 2008.
- Paul C. Rizzo Associates, a leading global engineering and consulting firm based in Pennsylvania, worked on site placement and engineering during the planning process.

Carbon Capture

The UAE is developing carbon capture technologies to enable oil and gas development while protecting the environment.
- In 2016, Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) built the region’s first industrial scale carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) facility. It captures 800,000 tons of carbon dioxide with plans to expand sixfold by 2030.
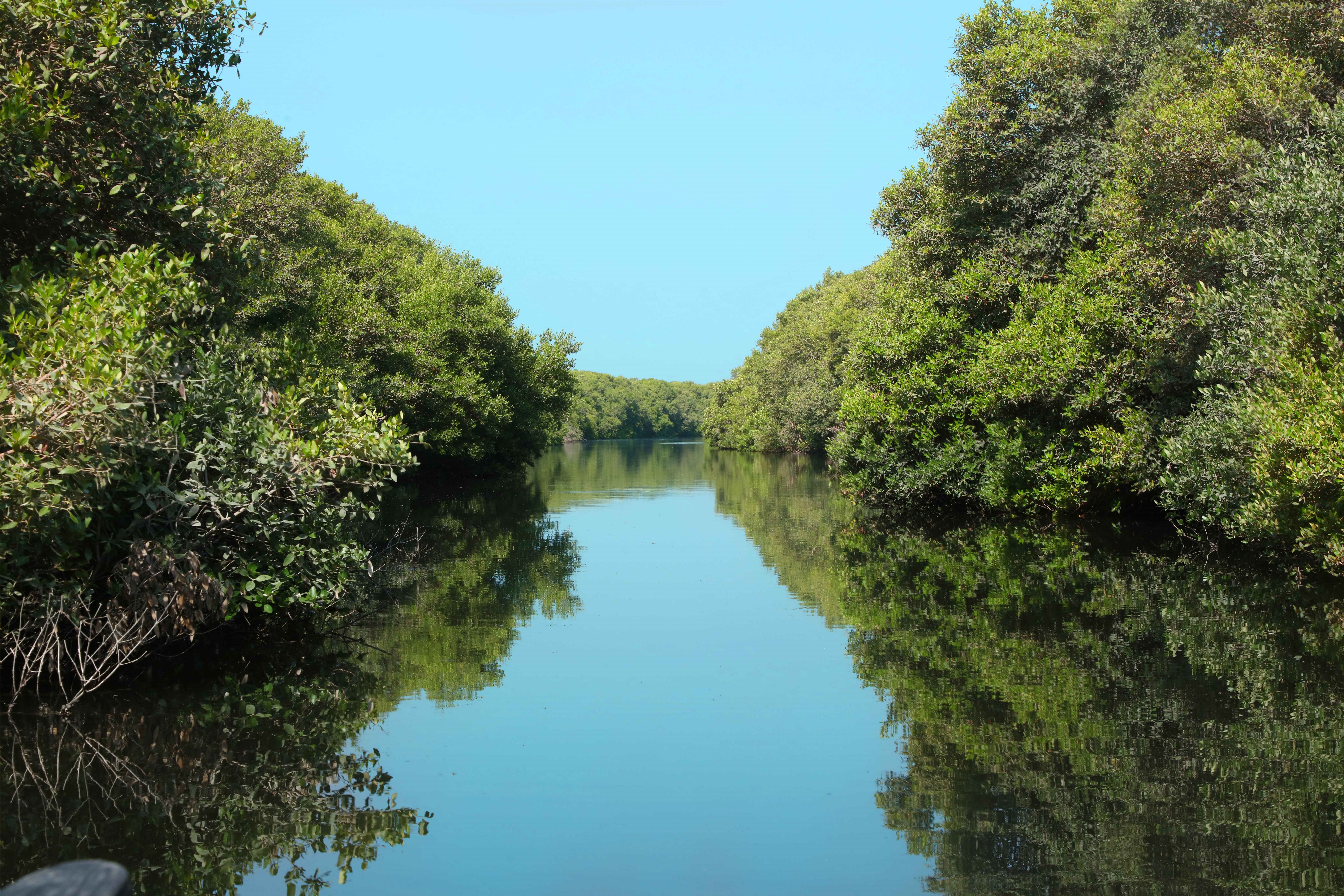
- The UAE is significantly expanding the country’s mangroves, which have the triple benefit of preventing coastal erosion, encouraging biodiversity and capturing more carbon per hectare than rainforests. The UAE plans to plant 100 million new mangroves by 2030.
- The carbon intensity of the UAE’s crude-grade Murban is less than half the industry average, and ADNOC is committed to reducing the carbon intensity of its operations a further 25 percent over the next decade. ADNOC is the only national oil company to source 100 percent of its grid electricity from zero-carbon nuclear and solar power.
Hydrogen
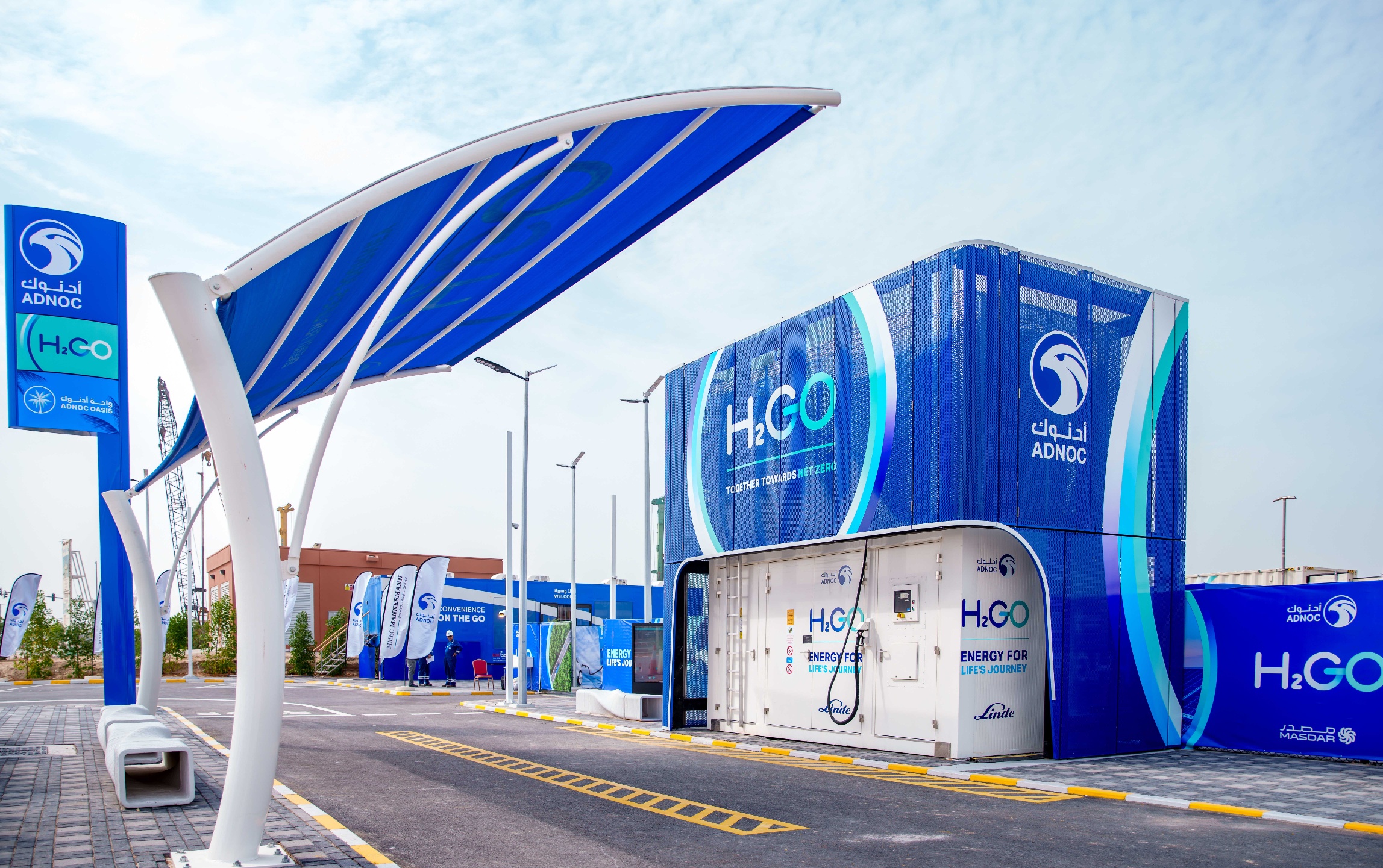

Hydrogen is a fuel that can be produced from a variety of domestic resources, such as natural gas, nuclear power, biomass and renewable power like solar and wind. It can be used in a wide range of applications, including in cars and homes. The UAE produces natural gas, which it can use to develop blue hydrogen. It also has ample sunshine, which can be harnessed to make green hydrogen.
- Launched at COP26 in November 2021, the Hydrogen Leadership Roadmap is a comprehensive national blueprint to support domestic, low-carbon industries and establish the UAE as a competitive exporter of hydrogen.
- In January 2021, the UAE launched the Abu Dhabi Hydrogen Alliance, comprised of ADNOC, Mubadala and ADQ, which will advance low-carbon green and blue hydrogen in emerging international markets and help build a substantial green hydrogen economy in the UAE.
- Dubai opened the first hydrogen filling station in the Middle East in October 2017.


